Applied Surface Science, 545, 148964, 2021
Surface-dependent photocatalytic and biological activities of Ag2CrO4: Integration of experiment and simulation
Marcelo Assis, Camila C. de Foggi, Vinicius Teodoro, João P. C. da Costa, Carlos E. Silva, Thaiane Robeldo, Priscila F. Caperucci, Carlos E. Vergani, Ricardo C. Borra, Ivan Sorribes, Amanda F. Gouveia, Miguel A. San-Miguel, Juan Andrés, and Elson Longo
Abstract
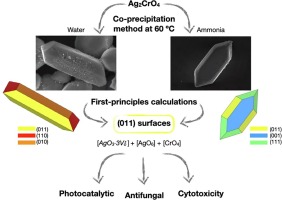
In this work, we present a joint experimental and theoretical study towards unveiling the photocatalytic (photodegradation of Rhodamine B), the antifungal (towards Candida glabrata) and cytotoxicity (against the L929 cell line) of Ag2CrO4. X-ray diffraction, Rietveld refinements, micro-Raman, UV–Visible spectroscopies, and photoluminescence emissions have been employed to characterize the as-synthetized samples by a co-precipitation method in water and ammonia. To complement and rationalize the experimental results, first-principles calculations have been performed within the framework of density functional theory. The crystal morphologies were characterized by field emission scanning electron microscopy images, while the Wulff construction, obtained by the calculated values of the surface energy, was employed to model and match the experimental images by tuning the relative stability of the exposed surfaces. This experimental and theoretical study provides a detailed understanding of the transformations of morphology and can aid in the development of the surface-dependent photocatalytic and biological activities of Ag2CrO4. We believe that our results offer new insights regarding the local coordination of superficial Ag and Cr cations on each exposed surface of the corresponding morphology, provided some general principles for material design, that dictate the properties of Ag2CrO4, a field that has so far remained unexplored.
